Did you know that untreated gum abscesses turn into severe dental abscesses in more than 40% of cases within just a few weeks ? Gum abscesses and dental abscesses aren’t just painful—they’re oral emergencies with the potential to cause rapid, sometimes permanent, tooth and bone loss if not managed swiftly and the right way. In this comprehensive, easy-to-understand guide, we’ll reveal how to treat periodontal abscess, when to seek help, and the crucial steps that keep both your smile and overall health protected. Your path to effective, urgent abscess treatment starts here.
Periodontal Abscess in Numbers: Why Immediate Abscess Treatment Matters
-
Did you know that untreated gum abscesses can lead to severe dental abscesses in over 40% of cases within just weeks? Discover the critical facts about how to treat periodontal abscess and why quick, proper intervention is crucial to oral health.
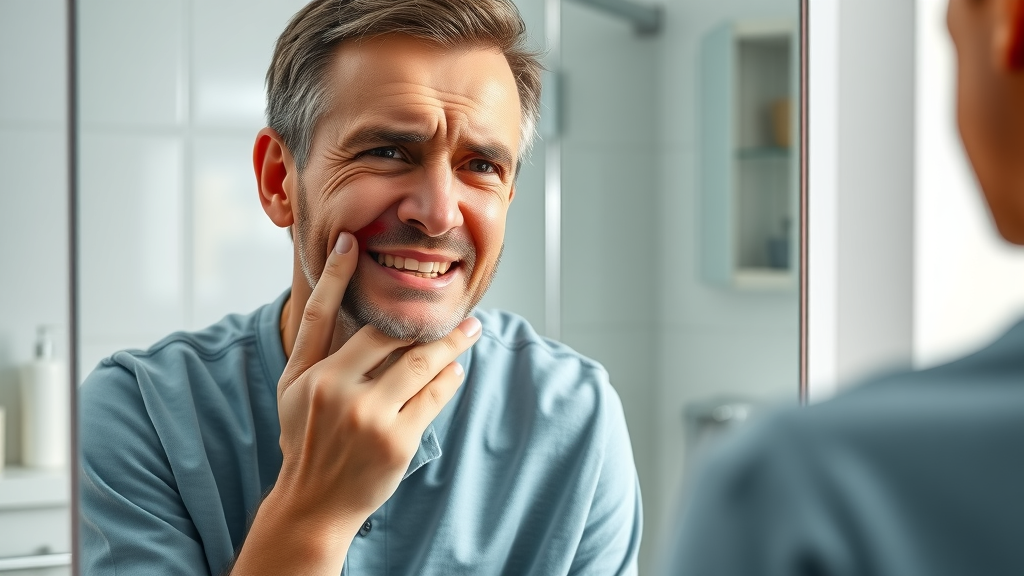

Immediate action for periodontal abscess is not just advice—it's a dental imperative. Data shows that when a gum abscess goes untreated, it can escalate to a more severe dental abscess in as little as a few weeks for almost half of affected adults. This rapid progression puts you at high risk of tissue and even bone damage. If ignored, a tooth abscess or periapical abscess may develop, threatening not just your tooth but potentially allowing infection to spread to other parts of your body. That’s why understanding how to treat periodontal abscess promptly can make the difference between keeping your teeth and facing extensive dental procedures.
The urgency of abscess treatment is clear: rapid intervention dramatically boosts your chances of recovery, reduces pain, and helps you avoid complicated procedures like root canal treatment or even extraction. By getting ahead of the infection through early recognition and timely dental care, you gain control over the outcome. Prevention and quick response are your best bets for long-term oral health and a pain-free future.
Understanding How to Treat Periodontal Abscess: Definitions and Key Concepts
-
What is a periodontal abscess?
-
Types: gum abscess, periapical abscess, dental abscess
-
What makes gum abscess different from dental abscess and periapical abscess?
-
The role of abscess treatment in oral health
A periodontal abscess is a pocket of pus that develops in the spaces around your teeth and gums. This occurs when bacteria invade deep periodontal pockets, triggering infection, swelling, and pain. Unlike a periapical abscess —which develops at the tip of the tooth root due to infected tooth pulp—a gum abscess forms within the soft tissue between your tooth and gum. The broader term, dental abscess , can apply to both types.
Understanding these differences is vital for targeted abscess treatment . A gum abscess typically stems from food impaction or trauma weakening the gum tissue. A periapical abscess is often the result of deep tooth decay or cracks that allow bacteria to reach the tooth pulp. Both demand different dental approaches for effective healing.
“Periodontal abscesses are among the top oral emergencies in adults—prompt professional care is essential to prevent tooth loss,” states Dr. Michelle Lim, DMD.
Effective abscess treatment goes beyond pain relief: it preserves your oral health , prevents the infection from spreading, and protects the integrity of both your teeth and gums . Only by recognizing symptoms and seeking help swiftly can you stop the infection, avoid more invasive procedures, and keep your smile for years to come.
What Causes Periodontal Abscess and How Does Abscess Treatment Work?
-
Common causes: poor oral hygiene, untreated gum disease, trauma, food impaction
-
Key risk factors for developing a dental abscess or gum abscess
-
Summary table: Causes vs. Risk Factors
-
How bacteria lead to the formation of periodontal abscess
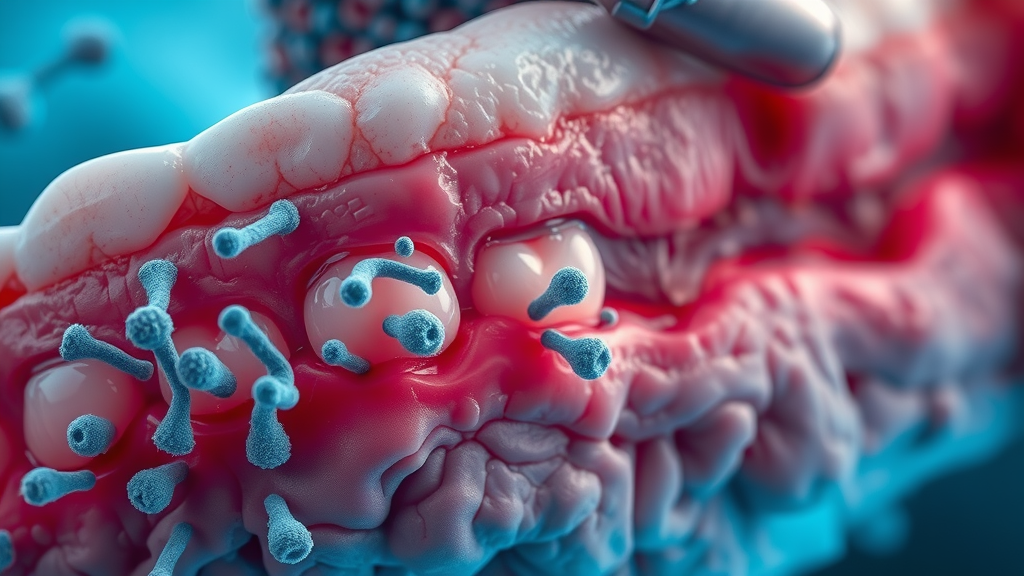
The main driver behind a periodontal abscess is the accumulation of harmful bacteria that thrive in deep gum pockets or around the tooth root . Causes often include poor oral hygiene like infrequent brushing or flossing, allowing plaque and food particles to lodge between teeth and gums. When these particles aren’t cleared away, bacteria multiply and penetrate the soft gum tissue, inciting a powerful immune response. The result is a pus-filled swelling or pocket of infection .
Untreated gum disease (also known as periodontitis) significantly elevates the risk. Trauma from hard brushing, accidental injury, or even aggressive flossing can create abrupt openings for bacteria. Food impaction—where tough or sticky foods get stuck between teeth—also creates a trap for bacteria and can kickstart an infection. Risk factors heighten with diabetes, smoking, existing dental conditions, or a history of abscessed tooth and prior dental abscesses .
Abscess forms when bacteria break through the gum surface or invade a periodontal pocket. If the infection remains unchecked, it can burrow deeper along the tooth root and into surrounding bone, leading to potentially serious damage that challenges even advanced abscess treatment options.
Addressing the root causes of gum and tooth infections is essential for lasting oral health. For individuals who have experienced significant tooth loss or damage due to untreated abscesses, exploring restorative solutions such as dental implants can help restore both function and aesthetics while preventing future complications.
|
|
|
Table: Periodontal Abscess Causes and Related Dental Abscess Risks |
|
Primary Cause |
Associated Risk Factors |
Potential Outcome if Untreated |
|---|---|---|
|
Poor oral hygiene |
Plaque buildup, irregular brushing, infrequent flossing |
Gum abscess, periodontal abscess, tooth abscess |
|
Untreated gum disease |
History of periodontitis, missed dental visits |
Loss of gum tissue, bone loss, tooth loss |
|
Trauma/injury |
Brushing too hard, dental procedures, injury from eating |
Acute gum abscess, secondary infection |
|
Food impaction |
Irregular flossing, tight teeth spacing |
Localized infection, chronic periodontal pocket |
|
Systemic conditions |
Diabetes, smoking, immunosuppression |
Recurrent abscess, slower healing |
Symptoms of a Periodontal Abscess: Identifying an Acute Dental Abscess
-
Signs and symptoms: pain, swelling, pus discharge, gum redness
-
Differentiating between gum abscess, periapical abscess, and tooth abscess
-
When to seek emergency abscess treatment
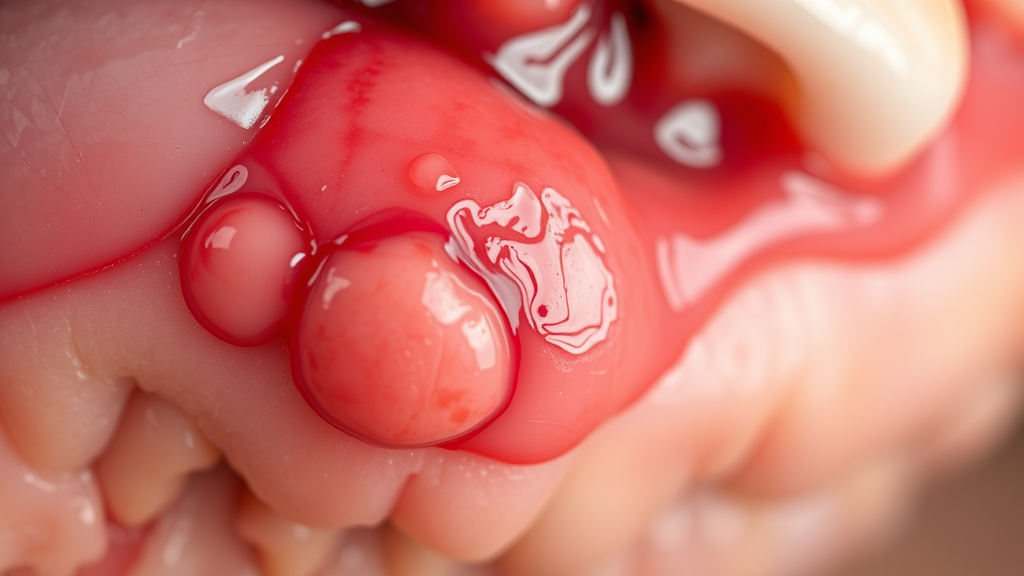
The warning signs of a periodontal abscess can strike suddenly or build up over time. The most common symptoms include persistent, often throbbing pain near the affected tooth, pronounced swelling of the gums , and visible redness or tenderness in the region. As the infection worsens, a pocket of pus may form, which can sometimes burst and ooze foul-tasting fluid. You might also notice increased tooth sensitivity, difficulty biting down, or even a raised, swollen bump along the gumline.
It’s crucial to distinguish between a gum abscess (affecting gum tissue directly), a periapical abscess (centered at the tip of the tooth root ), and a general dental abscess (which may involve both gum and bone). A gum abscess usually produces visible, swollen, reddened tissue near the gum margin, while a periapical abscess is most likely to cause intense pain and swelling closer to the lip or jaw, often with possible tooth movement.
If you encounter severe pain , swelling that rapidly increases, fever, chills, or signs of infection spreading (such as difficulty swallowing or breathing), you should seek emergency abscess treatment immediately . Ignoring these symptoms puts you at risk for much greater damage—not just to the teeth and gums, but potentially to other parts of your body as the infection can spread.
“Ignoring a periodontal abscess can accelerate tissue and bone loss around teeth,” warns the Cleveland Clinic.
Immediate Steps: How to Treat Periodontal Abscess at Home Before Dental Abscess Treatment
-
Rinsing and oral hygiene steps for gum abscess care
-
What NOT to do: Misconceptions about abscess at home remedies
-
When to use over-the-counter pain relief
-
Home care vs. professional periodontal abscess management
If you suspect a periodontal abscess , immediate home care can help manage pain and control infection while you prepare to see a dentist. Begin by rinsing your mouth with a warm saltwater solution several times daily. This simple step may reduce bacterial load and soothe inflamed tissues. Maintain impeccable oral hygiene : gently brush your teeth and floss to remove plaque and food debris—avoiding aggressive pressure near the abscessed area.
Resist the urge to attempt abscess drainage at home . Popping or squeezing a gum abscess can actually worsen the infection, push bacteria deeper, or cause severe tissue damage. Stick to using over-the-counter pain relief such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen as directed for temporary comfort, but recognize that this does not replace medical treatment. Never apply home remedies like herbal poultices, hydrogen peroxide, or undiluted essential oils to your gums—all of which may cause burns or complications.
Home management for gum abscess and periodontal abscess is strictly temporary , acting as a bridge until you receive professional dental care. Remember, only a dentist can definitively stop the infection and prevent permanent damage .
Safe and Unsafe Ways to Manage a Gum Abscess at Home
-
Cold compresses
-
Rinse with salt water
-
Avoid DIY abscess drainage
-
Myths about drawing out infection
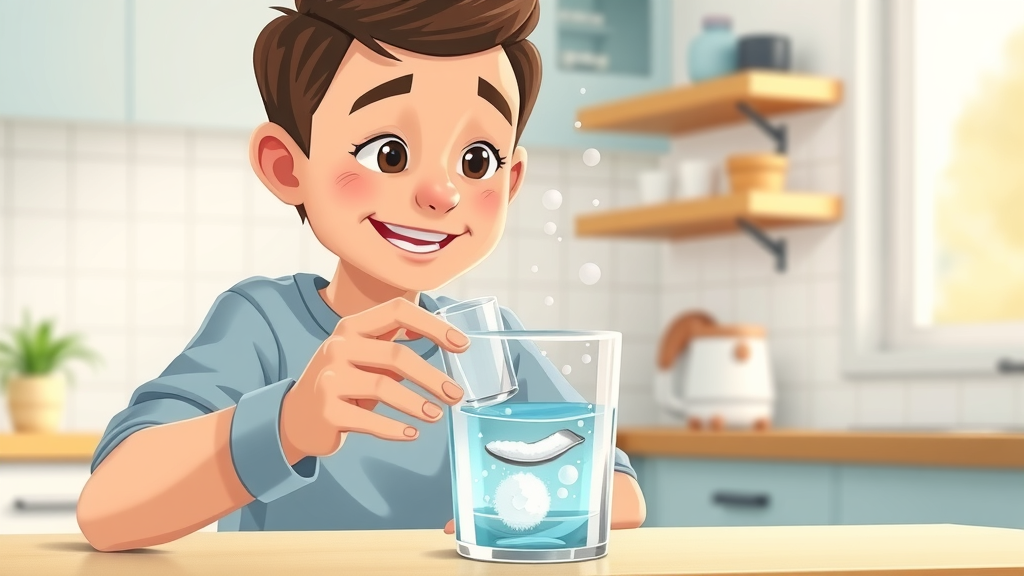

Safe home care for a gum abscess centers on minimizing inflammation while awaiting dental treatment. A cold compress applied to the cheek (never directly to the gum) can help ease swelling and numb pain. Regularly rinsing with a mild saltwater mix remains the most evidence-backed abscess at home remedy, supporting healing and potentially bringing some relief from pressure.
Never attempt to drain a gum abscess at home. DIY drainage, often promoted online, almost always worsens the problem, introducing more bacteria and heightening the risk of complications. Also, myths such as “drawing out” infection with home poultices have no medical backing and can result in further irritation or a spreading infection.
Ultimately, over-the-counter remedies provide only short-term comfort—not a cure. The only safe and effective way to eliminate a pocket of infection is through professional abscess treatment by a qualified dentist.
Professional Abscess Treatment: How Do Dentists Treat Periodontal Abscess?
-
Steps a dentist takes: diagnosis, cleaning, drainage, medication
-
Root canal vs. periodontal therapy for abscess treatment
-
How abscess treatment differs for periodontal abscess, gum abscess, and periapical abscess

Professional abscess treatment is tailored to the specific type—whether a gum abscess , periodontal abscess , or periapical abscess . Dentists begin by performing a thorough examination, possibly including X-rays, to identify the exact abscess site and evaluate surrounding tissues and bone. Next, the area around the abscess is cleaned, and drainage is performed when necessary to evacuate pus and stop the infection’s spread.
Dental abscesses may require antibiotics to control any spreading infection and reduce systemic risks, especially if swelling and fever are present. For deeper infections, a root canal is recommended if the tooth pulp is involved, while advanced periodontal therapy may be necessary for infections rooted in gum and bone tissue. Periapical abscess cases generally focus on saving and disinfecting the inner tooth, while periodontal abscesses often receive surgical cleaning and laser therapy when regular deep cleaning is not enough.
Tooth extraction may be a last resort if the infection is too severe to save the tooth. No matter the cause, professional abscess treatment is critical: it eliminates infection, relieves pain, and restores your path to healthy, functional teeth and gums.
Root Canal or Periodontal Surgery: Choosing the Right Dental Abscess Solution
-
When is root canal recommended over other treatments?
-
Surgical options for chronic periodontal abscess
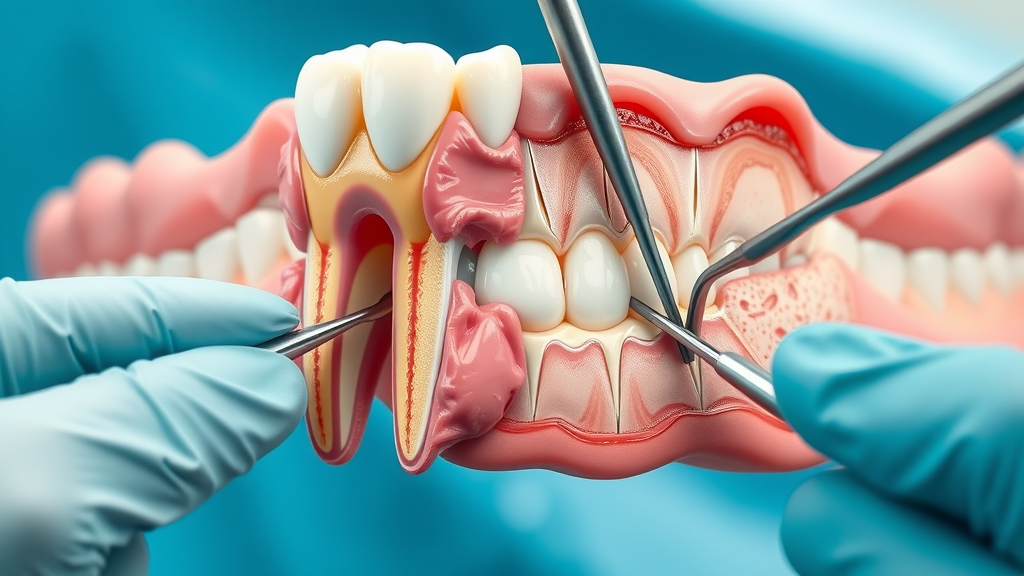
A root canal is called for when a periapical abscess has developed—meaning the infection has traveled to the tooth pulp or deepest tooth root. The procedure removes diseased tissue, thoroughly cleanses the root canal system, and seals the tooth to keep bacteria out. This is often the preferred approach to save your natural tooth when the infection is focused in the root apex.
Chronic periodontal abscesses involving extensive gum and bone tissue loss may require periodontal surgery. This could involve opening the gum to clean deep periodontal pockets , removing infected tissue, and promoting regeneration of bone and ligaments around the tooth. In some advanced cases, surgery is combined with grafts or advanced regenerative materials. Choosing between root canal and surgery depends on the extent, location, and source of infection—your dentist will determine the best treatment to stop the infection and preserve oral health.
Advanced Periodontal Abscess Management and Prevention
-
Preventive dental practices to reduce risk of gum abscess or tooth abscess
-
Professional deep cleaning and antibiotics
-
Prognosis of dental abscesses with early abscess treatment
-
Checklist: Preventing recurrence of periodontal abscess and gum abscess
“Routine dental visits are key to preventing severe abscesses and protecting your health,” – Cleveland Clinic.

The best treatment for periodontal abscesses is often prevention through good oral hygiene and regular dental care. Effective steps include brushing your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing to clear food impaction and bacteria between teeth, and using antibacterial mouthwash as advised by your dentist. Regular dental checkups ensure early detection and prompt management of developing gum disease or pocket of infection before they turn into full-fledged abscesses.
If you’ve already experienced a gum abscess or dental abscess , prevention is even more critical. Deep cleaning or scaling and root planing by your dentist removes embedded bacteria below the gums and discourages future infections. People at higher risk—such as those with diabetes, smokers, or individuals with previous abscesses—may need more frequent cleanings and tailored prevention plans. Antibiotics may be used for severe or systemic infections, but maintenance care is the true hero in stopping recurrences.
-
Brush your teeth and gums gently twice a day
-
Floss daily to remove trapped food particles
-
Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash
-
Never ignore signs of gum swelling, pain, or redness
-
Keep all dental appointments—even if you feel fine
-
Avoid smoking and manage chronic health conditions
-
Immediate professional care for any oral infection symptoms
Timeline Table: What to Expect During Periodontal Abscess Healing
|
|
|
|
Table: Periodontal Abscess Treatment Timeline—From Diagnosis to Full Recovery |
|
Step |
What Happens |
How Long? |
Expected Signs |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Day 1: Diagnosis |
Clinical exam, X-ray, abscess identified |
Same day |
Pain, swelling, pus present |
|
Day 1–2: Initial Treatment |
Pus drained, area cleaned, medication started |
1–2 days |
Immediate pain relief, swelling may reduce |
|
Day 3–7: Follow-up |
Monitor healing, further treatment if needed (root canal/surgery) |
Within 1 week |
Decreasing redness, healing under way |
|
Week 2–4: Recovery |
Tissue heals, infection clears, pain free |
2–4 weeks |
No swelling or tenderness, gums healthy |
|
After 1 Month: Prevention |
Ongoing oral hygiene and dental checkups |
Indefinite |
Abscess does not return, oral health stable |
-
How long does abscess treatment take for gum abscess?
-
Signs of recovery versus complications
Healing from a gum abscess or periodontal abscess can be rapid with early intervention. Simple cases respond to initial drainage and medication within a few days, and complete gum health often returns within 2–4 weeks. Signs of good recovery include reduced swelling, disappearance of pus, and restored gum color and texture.
On the other hand, persistent pain, continued swelling, or signs of spreading infection mean prompt follow-up is essential. Never hesitate to contact your dental provider if you notice symptoms returning— abscesses can recur if underlying causes aren’t fully addressed.
People Also Ask: Will a Periodontal Abscess Go Away?
-
Learn why a periodontal abscess rarely goes away on its own and why professional abscess treatment is necessary to resolve infection and prevent further dental abscess complications.
A periodontal abscess almost never disappears without professional treatment. While pain or swelling may seem to subside temporarily if the abscess ruptures on its own, the source of infection remains—meaning the problem can worsen, return, or spread, becoming far more dangerous. Only a dentist can fully eliminate all infected tissue, clean the periodontal pocket , and ensure complete healing. Quick, professional abscess treatment is the safest path to protect your teeth, gums, and overall health.
People Also Ask: How Do Dentists Treat Periodontal Abscesses?
-
Dentists diagnose the abscess location, perform drainage if necessary, thoroughly clean the area, and often prescribe antibiotics or recommend root canal if the infection has spread. The specifics depend on whether it is a gum abscess, periodontal abscess, or periapical abscess.
Dentists take a careful, stepwise approach: first, they determine the abscess type and location— gum abscess , periapical abscess , or both. Immediate relief is provided by draining the abscess , clearing away pus, and thoroughly cleaning the affected area. Antibiotics might be prescribed if the infection threatens to spread or enter the bloodstream. More extensive cases, especially with tooth root involvement, may require a root canal to eliminate all sources of bacteria. Only a professional can match the treatment to your specific needs and ensure safe, lasting recovery.
People Also Ask: What Is the Fastest Way to Get Rid of a Gum Abscess?
-
The fastest way to resolve a gum abscess is immediate professional dental care, which can provide safe drainage, thorough cleaning, and appropriate medications for rapid symptom relief.
If you want the fastest, most effective relief from a gum abscess , see a dentist as soon as symptoms appear. Quick professional action—drainage, cleaning, and medication—addresses the cause and not just the symptoms. Over-the-counter painkillers or rinses may provide momentary relief, but only dental intervention can decisively eliminate an active infection and stop it from progressing to a more severe dental abscess .
People Also Ask: How to Drain a Periodontal Abscess?
-
Draining a periodontal abscess should only be performed by dental professionals using sterile techniques to prevent spread of infection, tooth abscess progression, and ensure complete healing. Do not attempt drainage at home.
Do not attempt to drain a periodontal abscess at home. Only a qualified dental provider has the training and tools to safely evacuate pus, sterilize the site, and prevent infection spread. Trying DIY methods at home bears serious risks—including worsening the abscess, causing gum or bone damage, or pushing the infection further into your bloodstream. Always trust a dental professional for safe, successful abscess treatment .
FAQs on Periodontal Abscess, Gum Abscess, and Dental Abscess Treatment
-
What are the risks if a gum abscess is untreated?
-
Can antibiotics alone cure a periodontal abscess?
-
How does abscess treatment differ between a periapical abscess and a gum abscess?
-
Can a dental abscess recur after treatment?
-
What does a dental abscess feel like?

What are the risks if a gum abscess is untreated? An untreated gum abscess can quickly lead to bone loss, tooth loss, or spread to other parts of the body. The infection can worsen and become more challenging—sometimes threatening your general health.
Can antibiotics alone cure a periodontal abscess? Antibiotics may help control the infection temporarily, but they cannot cure a gum abscess on their own. Physical removal of pus and thorough cleaning by a dentist are always necessary for complete resolution.
How does abscess treatment differ between a periapical abscess and a gum abscess? A periapical abscess typically requires a root canal to clean the infected tooth pulp and avoid extraction. A gum abscess is managed through local drainage and cleaning of the gum space, with additional periodontal therapy if chronic gum disease is present.
Can a dental abscess recur after treatment? Yes, if underlying issues such as gum disease, poor oral hygiene, or unaddressed trauma are not corrected, a dental abscess can return. Ongoing care and regular dental visits are critical to prevention.
What does a dental abscess feel like? Typical symptoms include sharp, intense pain (especially on biting), continuous throbbing, gum swelling, redness, a visible bump, and sometimes a bad taste if the abscess drains. Severe cases may lead to fever, swollen lymph nodes, or difficulty opening your mouth.
Key Takeaways: Your Step-by-Step Guide on How to Treat Periodontal Abscess
-
Never ignore symptoms—prompt abscess treatment is vital
-
Understand the difference between gum abscess, dental abscess, and periapical abscess
-
Prevention is possible with regular oral care and professional cleanings
Contact the Experts: Professional Help for Periodontal Abscess Treatment
-
If you notice symptoms or require urgent abscess treatment, contact
-
Johnstown Dental Care at 370 West Coshocton St. Johnstown, OH 43031,
-
Phone: (470) 967-6046, or
-
visit www.johnstowndentalcare.com .
-
Proudly serving Johnstown, New Albany, Granville, Alexandria, Pataskala, and surrounding areas in Licking County, Franklin County, and Delaware County.
Take action at the first warning signs of a periodontal abscess: schedule an appointment with a dental professional to protect your smile before it's too late!
Mastering the essentials of periodontal abscess treatment is a powerful step toward lifelong oral health, but prevention and restoration go hand in hand. If you’re interested in a broader perspective on how advanced dental solutions can transform your smile after infection or tooth loss, discover the benefits of modern dental implants and their role in comprehensive oral rehabilitation . Exploring these options can help you regain confidence, function, and peace of mind—ensuring your dental health journey continues with strength and resilience.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment