Did you know that nearly half of all individuals with oral piercings will experience some form of tooth or gum damage within just one year? That’s a number worth chewing over. With the popularity of lip, tongue, and other mouth piercings on the rise, understanding how these trends impact your teeth and gums is more important than ever. If you’ve ever asked, “What about oral piercings and my teeth?,” this comprehensive guide uncovers the essential facts, risks, expert perspectives, and best practices to keep your oral health at its best—even with oral jewelry.
Unveiling the Truth: Oral Piercings, Teeth and Gums—What the Numbers Reveal
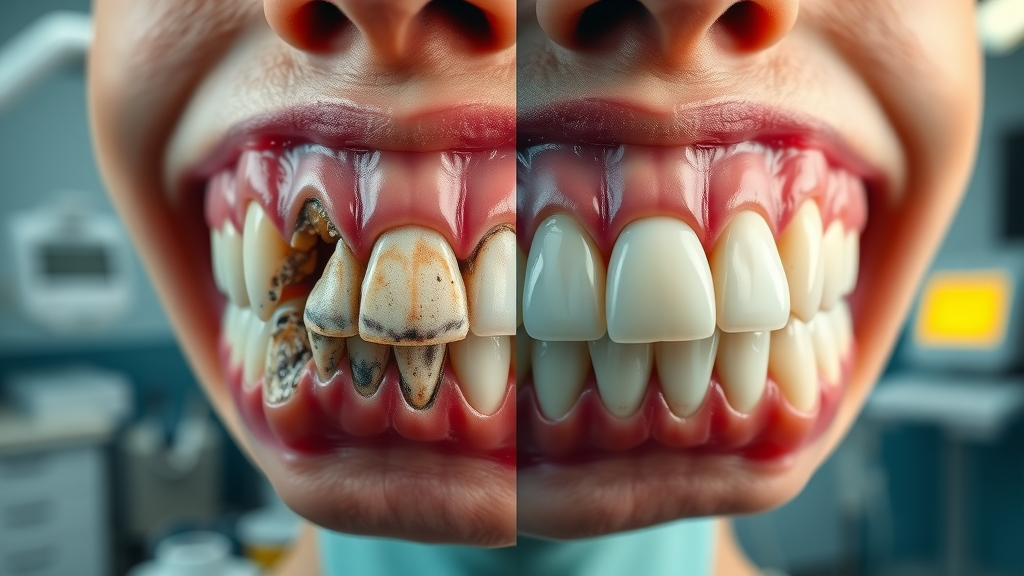
Oral piercings have exploded in popularity over the last decade, especially among teens and young adults seeking self-expression and individuality. But the statistics reveal a concerning side effect: the oral cavity is a delicate ecosystem, and even a small disruption—such as a piercing—can have major consequences for your dental health. According to clinical studies, nearly 50% of people with lip or tongue piercings experience complications like chipped teeth, gum recession, or even nerve damage within just twelve months.
The American Dental Association and numerous dental health professionals continuously stress that oral jewelry acts as a chronic irritant in the mouth. These concerns aren't hypothetical. After piercings, millions of bacteria can colonize the piercing site, and repeated metal-on-tooth contact frequently leads to tooth damage, from minor enamel wear to full-thickness dental fractures. Yet, not all risks are visible—some manifest as subtle gum tissue changes or sensitivity, altering your oral comfort and function over time.
If you're considering joining the ranks of those with mouth piercings, or already have one, it's crucial to weigh how such body modifications can impact your oral health, and to understand the preventative steps that can safeguard your smile.
For those who are already experiencing dental complications or are concerned about long-term effects, exploring restorative options such as dental implants can be an important consideration. Dental implants offer a reliable solution for replacing teeth that may be lost or severely damaged due to oral piercings or other factors, helping you restore both function and aesthetics.
Startling Facts: How Oral Piercings Impact Teeth and Oral Health – A Deep Dive
Scientific reviews and clinical evidence point to a direct link between oral piercings and oral healthcare complications. For instance, vigorous movement or habitual clicking of tongue or lip piercings can accelerate enamel wear and eventually result in permanent tooth loss or unrepairable tooth fractures. This risk extends to both premolars and front teeth, where contact is frequent, leading to increased tooth sensitivity and a higher chance of gum recession—in which the soft tissue pulls away from the tooth, exposing sensitive roots and increasing the risk of infection.
It’s not only the hard tissues that suffer. Chronic friction from oral jewelry can create pressure points, damaging the gum tissue and leading to gum disease or inflammation. Infection at the piercing site is another well-documented issue, with millions of bacteria in the mouth ready to invade any new opening. As the Journal of Clinical Dentistry states, nearly half of oral piercing wearers experience unmistakable signs of oral deterioration within a year—making the risks of body modification very real.
- The relationship between oral piercings and your teeth and gums
- Risks associated with common piercings like lip and tongue piercings
- How to maintain optimal oral hygiene with oral piercings
- Preventative strategies to avoid nerve damage and gum recession
- Evidence-based answers to People Also Ask questions
Understanding the Basics: What About Oral Piercings and My Teeth — An Overview
If you’re new to oral body modification, you might ask, “What about oral piercings and my teeth? Why are dentists so concerned?” The answer is simple: your oral cavity is lined with sensitive gum tissue, loaded with nerves, and teeming with bacteria—making it especially susceptible to trauma and infection. Both lip piercings and tongue piercings are the most popular forms, but any mouth piercing carries the potential for oral health issues.
The structure of each piercing, its jewelry type, and placement all interact with your teeth and gums daily. From plaque accumulation at the jewelry base to repeated scraping against delicate tooth enamel, these daily mechanical and bacterial insults set the stage for gum disease, tooth damage, and other dental concerns. Recognizing the unique features—and potential risks—of different piercings is key to safeguarding your smile.
Types of Oral Piercings (Including Lip Piercings and Tongue Piercings)
Oral piercings come in many varieties, and each type affects your mouth—and your oral health—differently. Whether you favor a simple lip piercing or something more exotic like a uvula piercing, every style presents its own set of challenges for oral hygiene and maintenance.
- Lip piercings
- Tongue piercings
- Cheek piercings
- Frenulum piercings (upper lip or under-tongue webbing)
- Uvula piercings
- And more (including smiley, snake eyes, and surface piercings)
Oral Health Considerations with Mouth Piercings
Before opting for a mouth piercing, it’s essential to consider how it affects your oral health. Metal jewelry often rubs against the teeth and gums, leading to gum recession—a progressive pulling away of gum tissue that can expose tooth roots and increase sensitivity. Even plastic or biocompatible materials aren’t entirely risk-free, as they still trap bacteria and can cause chronic irritation or scar tissue formation.
Oral piercings also increase the risk of infection and inflammation. Your mouth provides a warm, moist habitat for millions of bacteria. When you introduce a piercing, you create an open door for germs to enter. Piercings heal slowly due to this environment—sometimes taking weeks or months—prolonging the risk of infection and other complications. Finally, repeated trauma from jewelry movement can create tiny wounds in the oral cavity, fueling more frequent outbreaks of pain, swelling, and bleeding that can threaten your overall dental health.
Risks and Complications: What About Oral Piercings and My Teeth?
While the aesthetic appeal of piercings draws many people in, awareness of the associated risks is crucial. Oral piercings can compromise your teeth and gums through daily mechanical stress, bacterial exposure, and chemical reactions to metals like nickel or chromium. Understanding these potential risks is the first step toward proactive prevention and safer body modification.
The repeated impact of oral jewelry, if unchecked, leads to common dental issues such as gum recession and chipping. But complications don’t stop there—allergic reactions, nerve damage, and prolonged muscle discomfort are realities that both new and longtime piercers need to confront. Developing habits to reduce the risk and working closely with dental professionals are key for anyone considering a mouth piercing.
Damage to Teeth and Gums from Oral Piercings
The most immediate harm from oral jewelry is to the teeth. Hard metal ball ends, barbells, and rings can chip or fracture enamel, leaving your smile vulnerable to sensitivity and decay. Tongue barbells, in particular, are prone to accidentally striking the incisors or molars—which can cause visible chips, cracks, or even complete breaks in the tooth structure. Additionally, repeated contact between jewelry and soft tissues results in gum recession and the development of scar tissue that can destabilize the tooth’s foundation.
For those who already have pre-existing dental issues, the risk of tooth damage from mouth piercings is even greater. Even a minor chip or hairline crack can compromise the strength of a tooth, and left untreated, may lead to the need for advanced dental care such as crowns, root canal treatments, or even extractions. The piercing site often becomes a trap for food debris and plaque, further increasing the likelihood of infection around both teeth and gums.
Gum Recession & Tooth Sensitivity from Lip Piercings and Oral Piercings
One of the stealthier consequences of oral piercings is gum recession. The persistent friction of jewelry against gum tissue causes the gums to slowly retract, exposing more of the tooth’s root. This not only detracts from the look of a healthy smile but also leads to strong tooth sensitivity, especially to hot, cold, or even sweet foods and drinks.
Compromised gums are less effective at protecting the underlying bone and connective tissue, opening the door for gum disease and even eventual tooth loss. People with lip piercings or tongue piercings often notice increased sensitivity and occasional bleeding. According to the Journal of Clinical Dentistry,
“Nearly 50% of people with oral piercings experience gum recession or chipped teeth within 1 year of placement.”
Nerve Damage, Allergic Reaction, and Infection Risks of Oral Piercings
Beyond surface-level complications, oral piercings put delicate nerves at risk. There’s a real potential for accidental trauma during piercing placement, which can result in nerve damage—manifesting as tingling, numbness, or chronic pain in the tongue, lips, or jaw. These symptoms may fade with time, but sometimes they persist, causing lasting discomfort and affecting your speech or eating.
Another under-appreciated risk is allergic reaction to certain metals used in oral jewelry, like nickel. These reactions can trigger swollen, itchy, or burning areas in the mouth, sometimes requiring urgent removal of the jewelry. Lastly, the open wound created by a fresh piercing increases the risk of infection, especially in the first weeks after placement. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, throbbing pain, and pus at the site. Immediate consultation with a dental professional is always advised if any of these emerge.
How to Protect Teeth and Gums: Oral Hygiene Best Practices for Piercings
- Regular cleaning protocols
- Suitable mouthwashes
- Best toothpastes for those with oral piercings
- Professional dental check-up frequency
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is critical for anyone with a mouth piercing. Diligent cleaning prevents the buildup of plaque—a sticky film of millions of bacteria—which can quickly lead to gum inflammation, infection, or tooth decay surrounding the piercing site. Incorporating anti-bacterial rinses and choosing the right toothpaste with gentle, non-abrasive ingredients can further reduce the risk to your teeth and gums.
Scheduling professional dental checkups at least every six months (and even more frequently for those with piercings) ensures early detection and management of any arising issues. Dentists can provide targeted advice, spot minute changes to gum tissue and enamel, and help you prevent small problems from evolving into major threats to your dental health.
Expert Guide: Oral Hygiene for Lip Piercings and Mouth Piercings
Caring for your teeth and gums with a lip piercing or other oral jewelry is a daily commitment. Brush gently twice a day with a soft-bristled brush, making sure to clean around the jewelry and the piercing site without causing additional irritation. Use antimicrobial mouthwash to flush away bacteria from hard-to-reach places, including under the jewelry. It’s wise to avoid mouthwashes with alcohol, as they can cause dryness and further irritate sensitive tissue.
Choosing biocompatible materials (like surgical steel or titanium) for your piercing can reduce the risk of allergic reaction. Flossing carefully each day, paying close attention to the gum line near the piercing, keeps plaque buildup and gum disease at bay. Finally, always inspect your mouth for signs of swelling, bleeding, or discharge, and never hesitate to consult your dentist at the first sign of trouble.
| Piercing Type | Risk to Teeth & Gums | Maintenance Level | Healing Time | Average Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lip Piercing | High risk of gum recession, tooth chipping | Moderate | 6-8 weeks | $40–$80 |
| Tongue Piercing | Highest risk: chipping, nerve damage | High | 4-6 weeks | $50–$100 |
| Cheek Piercing | Moderate risk, swelling, gum issues | High | 8–12 weeks | $60–$120 |
| Frenulum Piercing | Lower risk, still can cause gum irritation | Low-Moderate | 2–4 weeks | $30–$70 |
Expert Dental Perspective: What Dentists Say About Oral Piercings and Teeth
Dental professionals across the globe are increasingly raising red flags about the long-term effects of oral piercings. Their main concern? The sharp rise in tooth damage and gum recession tied directly to oral jewelry. Patients often visit their dentist only after experiencing pain, sensitivity, or visible chipping, when intervention is already urgent and the damage is sometimes irreversible.
“Dentists are seeing an increasing number of patients with damage caused by oral piercings, especially chipped teeth and receding gums.” — Dr. Adrian Mendez, DDSAmerican Dental Association
People Also Ask: Answering Common Questions About Oral Piercings and Teeth Health
Do oral piercings damage teeth?
Yes, oral piercings can damage teeth by causing chipping, enamel wear, and even fractures. They also increase the risk of gum recession and infection, impacting long-term oral health.
How do I keep my lip piercing from ruining my teeth?
To minimize risk, maintain strict oral hygiene, choose non-metallic jewelry, regularly inspect teeth and gums for early signs of damage, and visit your dentist frequently.
What do dentists say about lip piercings?
Most dentists caution against lip piercings due to a heightened risk of chipped teeth, gum recession, and infection, and recommend immediate dental consultation if any issues appear.
How to avoid ruining teeth with a tongue piercing?
Avoid biting down or playing with the tongue jewelry, use biocompatible materials, follow recommended cleaning procedures, and seek regular dental checkups to catch issues early.
Key Takeaways: Maintaining Oral Health with Oral Piercings
- Oral piercings pose real risks to teeth and gums
- Proper hygiene and professional oversight are mandatory
- Preventative practices can significantly reduce risks
- Dentist input is critical for safe, long-term oral health
FAQs: Oral Piercings and My Teeth
-
What are early symptoms of nerve damage from piercings?
Early symptoms can include numbness, tingling, persistent pain, or loss of sensation around the piercing site. If you notice these, consult a dental professional promptly to assess for nerve involvement. -
Are certain oral piercings safer than others?
Yes, piercings like the frenulum (tongue web) are typically less likely to cause significant gum or tooth damage, but all oral piercings come with infection and irritation risks. Placement and jewelry choice are key factors. -
Can I reverse gum recession caused by oral piercings?
Early gum recession can sometimes be managed with cessation of the cause and professional dental care, but advanced cases may require grafting or specialist intervention. Prevention is always easier than reversal. -
What materials are best for minimizing allergic reaction?
Choose jewelry made from surgical-grade titanium, surgical steel, or biocompatible plastics like PTFE. Avoid jewelry containing nickel, which frequently triggers allergic reactions in the oral cavity.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Oral Health—Is an Oral Piercing Worth the Risk to My Teeth?
Oral piercings may be trendy, but your teeth and gums are irreplaceable. Weigh the risk, consult your dentist, and put oral health first before making any decision—and remember, prevention always beats treatment.
Ready to Protect Your Teeth and Gums? Schedule a Dental Consultation to Discuss Oral Piercings Today
If you have, or are considering, any kind of mouth or oral piercing, the best way to protect your teeth and gums is with proactive dental care. Schedule a comprehensive check-up with your dental professional and review proper aftercare and materials. Your smile—and your health—will thank you.
If you’re interested in exploring more ways to enhance your smile while maintaining optimal oral health, consider learning about the latest advancements in orthodontic care. Modern solutions like clear aligners can help you achieve a straighter, healthier smile without compromising your personal style. Discover how aligning your teeth with confidence and comfort is possible by reading our in-depth guide on the clear choice in modern orthodontics. Taking the next step in your dental journey could be the key to a lifetime of healthy, beautiful smiles.
Oral piercings, such as those on the tongue and lips, can pose significant risks to dental health, including damage to teeth and gums. The jewelry is likely to knock against your teeth, chipping or fracturing them, and it will require professional attention to fix. (americandentalgroup.org) Additionally, the constant friction of a lip or tongue piercing against your gums can cause the gum tissue to pull away from your teeth, leading to gum recession. (denverdental.com) Understanding these risks is crucial for anyone with or considering oral piercings.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment