Did you know that nearly half of adults in the United States over age 30 show signs of gum disease? This silent epidemic often progresses unnoticed, but early detection and intervention can make all the difference. Whether you're newly diagnosed, experiencing advanced symptoms, or simply want to safeguard your oral health, understanding the full range of treatment options for gum disease is a vital step toward a healthier smile and a healthier you.
Millions Affected Annually: The Urgency Behind Seeking Treatment Options for Gum Disease
With millions of people impacted by gum disease every year, getting the right treatment options for gum disease has never been more urgent. Left untreated, gum disease can cause pain, bleeding gums , gum recession , and even tooth loss —all of which can severely affect quality of life. In fact, this common oral health issue doesn’t just threaten your teeth and gums, but can also increase your risk for wider health problems such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory concerns.
Practical examples of treatment include regular visits to a dental hygienist for professional cleanings, at-home care like thorough brushing and flossing , and targeted therapies depending on the stage and severity of disease. Recognizing early warning signs and understanding your options for gum disease treatment empowers you to act sooner, stop disease progression, and enjoy lasting results from your oral care routine.

Understand all available treatment options for gum disease
Identify effective gum disease treatments for every disease stage
Learn the goals of disease treatment and prevention
Recognize symptoms and risk factors for early intervention
Discover advanced therapies and surgical interventions for severe cases
Gum Disease Explained: What Is It and Why Treatment Options for Gum Disease Matter
Gum disease, or periodontal disease , is a progressive oral condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the tissues supporting the teeth. The progression of gum disease can be subtle, beginning with minor gum irritation and advancing to severe bone loss or even tooth loss if not properly managed. Treatment options for gum disease are critical not only for maintaining oral health but also for avoiding the potentially serious systemic consequences that can arise when the infection is left untreated. Proactive disease treatment helps preserve healthy gum tissue , prevents further progression, and can even reverse some of the damage in the early stages.
Understanding the nature of gum disease and its impactful role within total oral health is an essential first step in prevention. When gums become infected, the body’s immune response may target both the bacteria and the supporting structures of the teeth, leading to a breakdown of the gum line , recession, and weakening of the underlying bone. Early and consistent intervention is, therefore, the best defense against long-term consequences and the foundation for lifelong dental wellness.
Stages of Gum Disease and Their Impact on Oral Health
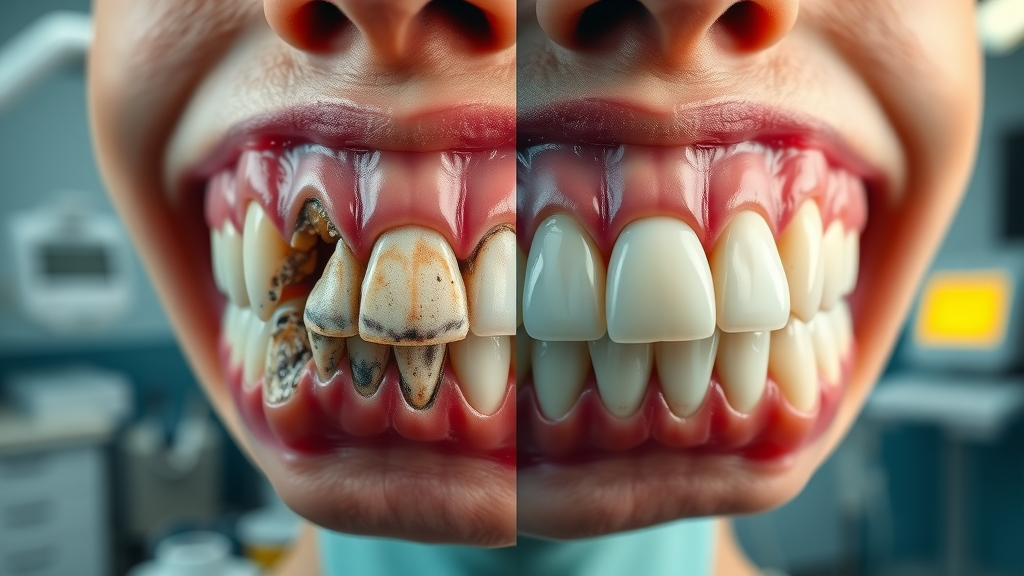
The journey of gum disease—from mild irritation to advanced periodontal disease —is marked by notable changes in symptoms and required interventions. The earliest stage, gingivitis , is often characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding gums but is generally reversible with timely care. If gingivitis is ignored, it can progress to periodontitis , where the infection penetrates deeper, impacting the bone and connective tissue. As the condition persists, chronic inflammation leads to bone loss and the formation of periodontal pockets, increasing the risk for tooth loss and more intensive treatment needs.
Each stage of gum disease presents differently, but all stages require dedicated attention and tailored gum disease treatment strategies. For example, scaling and root planing might suffice during early or moderate periodontitis, while severe cases may demand advanced surgical interventions like bone grafting or gum graft procedures. Recognizing the stage-specific impact on your oral health not only guides effective management but also helps prevent recurrence and complications.
Risk Factors That Accelerate the Need for Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Certain risk factors can drastically accelerate the need for treatment options for gum disease. These include smoking or tobacco use, poor oral hygiene , genetics, uncontrolled diabetes, hormonal changes, and even stress. Additionally, some medications and medical conditions may lower your body’s resistance to infection, making it easier for a form of gum disease to take root and progress rapidly. Systemic conditions such as heart disease also intertwine with oral health, making it critical to consider these risk factors during treatment planning.
Awareness is key—patients who understand their personal risk factors are more likely to seek preventive care and recognize early signs that require action. A family history of gum disease, certain illnesses, or a lifestyle that includes smoking or high sugar intake makes proactive screenings and professional treatments especially important. By identifying and addressing these risk factors , you can select the right therapies before irreversible damage occurs.
Progression of Periodontal Disease and Corresponding Treatment Options |
||
Stage |
Symptoms |
Recommended Treatments |
|---|---|---|
Gingivitis |
Redness, swelling, bleeding gums |
Professional dental cleaning, improved oral hygiene, antimicrobial rinses |
Early Periodontitis |
Pocket formation, mild gum recession |
Scaling and root planing, local antibiotic treatments |
Moderate Periodontitis |
Increased pocket depth, bone loss |
Deep cleaning, systemic antibiotics, reevaluation |
Advanced Periodontitis |
Severe gum recession, loose teeth, significant bone loss |
Surgical intervention (pocket reduction, gum graft, bone grafting, guided tissue regeneration) |
Initial Steps: Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Gum Disease
The first line of defense for gum disease treatment often involves non-surgical therapies aimed at reversing early symptoms and preserving oral health. These initial steps focus on halting the progression of disease by removing the underlying causes: plaque and tartar buildup at and beneath the gum line. Routine professional cleanings by a dental hygienist and a strict at-home routine typically form the basis of care for mild to moderate cases.
Additionally, non-surgical treatment options for gum disease include the use of antimicrobial mouth rinses, targeted antibiotics, and continuous monitoring to ensure the infection is under control. When paired with diligent daily practices such as brushing and flossing , these strategies can be remarkably effective in arresting disease progress before it causes irreversible tissue or bone loss.
For individuals facing more advanced stages of gum disease or those who have already experienced tooth loss, exploring restorative solutions such as dental implants can be an important part of comprehensive treatment planning. Dental implants not only restore function and aesthetics but also help maintain jawbone health after periodontal disease.
Deep Cleaning: Scaling and Root Planing for Gum Disease Treatment
Deep cleaning, known clinically as scaling and root planing , is a cornerstone of non-surgical gum disease therapy. This procedure involves your dental provider carefully removing plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces above and below the gum line. After scaling, root planing smooths the root surfaces to deter further bacterial buildup and facilitate gum reattachment. This approach is particularly effective in early and moderate stages of periodontal disease , where the goal is to eliminate infection without surgery.
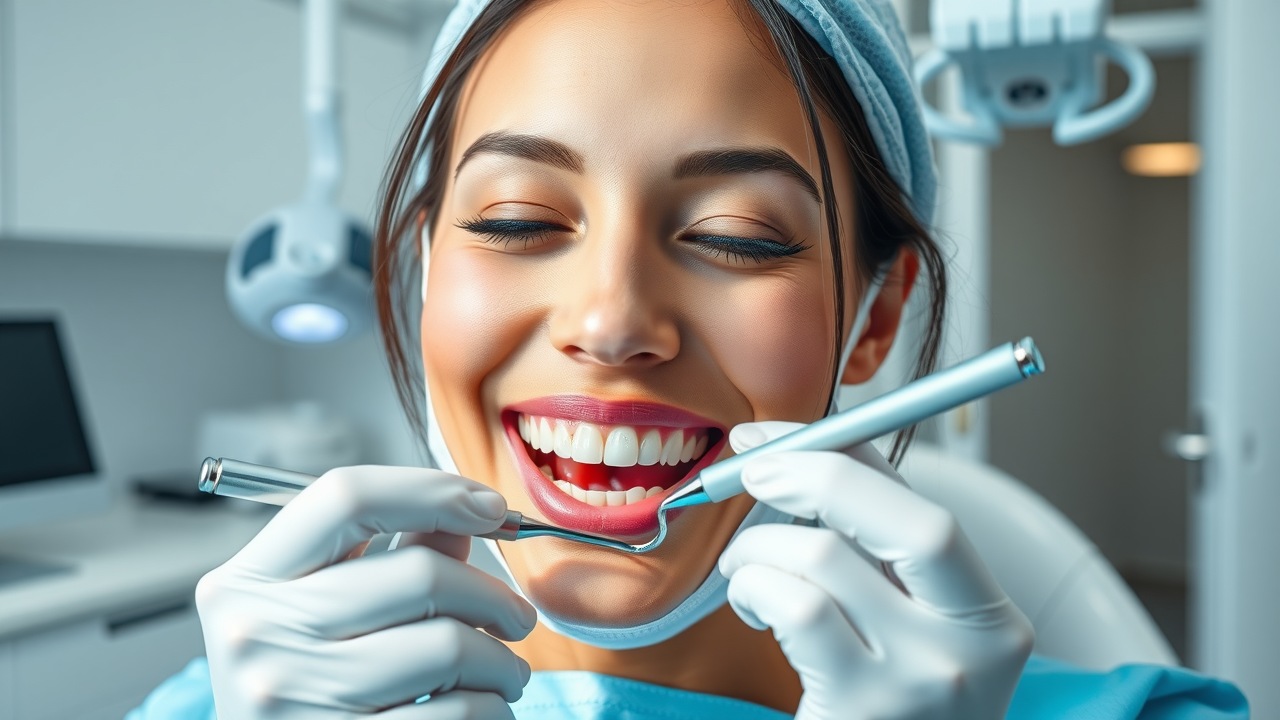
Root planning may require one or more visits, depending on disease severity and the number of affected areas. Patients may experience temporary sensitivity or minor discomfort, but the benefits—such as reduced bleeding, smaller periodontal pockets, and improved oral health —make this a highly recommended choice for many individuals. Maintaining excellent oral hygiene at home post-procedure is crucial to optimize results and prevent recurrence.
Medications Used in Disease Treatment: Antimicrobials and Antibiotics
Pharmacological approaches form a valuable adjunct to mechanical cleaning in gum disease treatment. Dentists may recommend antimicrobials (like chlorhexidine rinses) or locally applied antibiotics (such as minocycline microspheres) to target infection between teeth and within periodontal pockets. In some cases, systemic antibiotics may be prescribed for more aggressive or persistent infections.
These medications are designed to reduce bacterial populations that drive oral health decline and offer a way to manage sites inaccessible by mechanical cleaning alone. However, medication is usually not a stand-alone solution; it works best when combined with professional deep cleaning and consistent at-home care practices. Patient adherence and follow-up visits ensure the infection is eliminated and monitor healing progress.
Advanced Disease Treatment: Surgical Treatment Options for Gum Disease
When non-surgical techniques are insufficient—typically in cases of advanced periodontal disease with significant bone loss or tissue destruction—surgical intervention may be necessary. Treatment options for gum disease at this stage are designed to restore lost support structures, reduce deep pockets, and repair extensive damage. These advanced therapies require skilled periodontists and advanced technology, offering hope for even the most serious cases.
Surgical gum disease treatment options vary in complexity, ranging from procedures that focus on reducing periodontal pocket depth to sophisticated tissue regeneration techniques. The aim is not just to control infection, but to restore function and aesthetics by rebuilding lost tissues and supporting long-term stability for your teeth.
Pocket Reduction Surgery: Restoring Oral Health
Pocket reduction surgery , sometimes called flap surgery, is a key intervention when periodontal pockets have deepened beyond the range of non-surgical care. During this procedure, the gum tissue is gently lifted back to provide clear access for the removal of plaque and tartar from deep root surfaces. The area is then thoroughly cleaned, and, if necessary, the bone may be smoothed to eliminate rough spots that could harbor bacteria.
After cleaning, the gum tissue is repositioned snugly around the teeth, reducing the space where bacteria can accumulate and promoting an environment for healing. Pocket reduction not only controls infection but also supports easier maintenance of oral health and a reduced risk of relapse, ultimately preserving your natural teeth for as long as possible.
Gum Graft Procedures for Severe Gum Disease Treatment
Gum graft procedures address severe gum recession —one of the most visible consequences of advanced gum disease. When significant portions of the gum tissue are lost, sensitive root surfaces become exposed, heightening the risk for decay, sensitivity, and further bone deterioration. Gum grafting involves transferring healthy tissue (commonly from the roof of the mouth) to the affected site, covering exposed roots and rebuilding the gum line.
Patients benefit not only from improved smile aesthetics and reduced sensitivity but also from the protective effects the newly placed gum tissue offers against bacterial invasion. For those facing chronic periodontal disease complications, gum grafts can be a critical element fusing restoration with prevention to halt further damage and enhance oral health.
Bone Grafting and Guided Tissue Regeneration for Periodontal Disease
Advanced periodontal disease often leads to destruction of bone that supports your teeth, risking mobility or tooth loss. Bone grafting and guided tissue regeneration are surgical treatment options for gum disease that work to rebuild lost integrity. In a bone graft, natural or synthetic bone material is placed in the area of loss, acting as a scaffold for your body to regenerate new bone and restore the tooth’s foundation. This technique is particularly valuable after infection control or alongside pocket reduction surgery.
Guided tissue regeneration employs special membranes placed between the gum and bone, allowing only the bone to repopulate the area. This prevents fast-growing gum tissue from filling in before bone cells have a chance to regenerate. Together, these advanced interventions not only increase the likelihood of retaining natural teeth but also set the stage for long-term function and renewed oral health.
Watch: Animated Overview of Treatment Options for Gum Disease and Periodontal Disease Progression
Integrating At-Home and Professional Gum Disease Treatment for Lasting Results
A truly effective approach to gum disease treatment encompasses both professional therapies and diligent at-home maintenance. While dental visits are essential for diagnosis and advanced interventions, sustained prevention depends on your daily routine. Consistent brushing, flossing, and smart choices—such as avoiding tobacco and a high-sugar diet—play a crucial role in keeping gum disease at bay between appointments.
Patients who integrate advice gained from dental care professionals into their personal habits enjoy the greatest success. Education about proper technique, recognizing warning signs, and maintaining regular check-ups forms an ongoing partnership that results in lasting oral health improvements and minimizes the risk of future complications.
At-Home Maintenance and Prevention: Improving Oral Health
Your best defense against gum disease is a robust at-home care regimen. Brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush, using fluoride toothpaste, and daily flossing remain the gold standards for removing food debris and plaque and tartar before they can harden under the gum line. Antimicrobial rinses and interdental brushes can offer additional benefits, especially for those already managing gum disease or at increased risk.

Additional habits, such as a healthy diet rich in antioxidants and regular hydration, help reduce inflammation and support overall tissue healing. For those with known risk factors or those who have undergone non-surgical or surgical therapies, diligent at-home prevention not only preserves treatment results but also reduces the potential for recurrence—making it a cornerstone of comprehensive gum disease treatment.
When to Seek Professional Gum Disease Treatment
Prompt professional care is critical whenever you notice symptoms such as bleeding gums , persistent bad breath, gum line recession, swelling, or loose teeth. Waiting too long can allow disease progression to the point where advanced interventions, including surgery, become necessary. People with multiple risk factors —such as smokers, diabetics, or those with a family history—should be especially vigilant about early evaluation and seeking specialist consultation as soon as warning signs appear.
Dental check-ups every six months, or more frequently if you are at elevated risk, enable hygienists and dentists to detect problems early and recommend the most suitable treatment options for gum disease. Timely professional interventions halt ongoing tissue destruction, address underlying causes, restore oral function, and ensure that your smile remains healthy for years to come.
Complications When Delaying Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Delaying treatment for gum disease puts you at risk of far-reaching complications. Untreated infection can progress rapidly, causing extensive bone loss , chronic discomfort, shifting or loose teeth, and even complete tooth loss. The longer inflammation persists, the more difficult and invasive eventual treatments become, with poorer long-term outcomes and increased costs.
Beyond dental health, untreated gum disease can impact your entire body. Chronic oral infections may act as gateways for harmful bacteria to enter the bloodstream, triggering systemic inflammation and raising risks for conditions like heart disease, stroke, diabetes complications, and respiratory illnesses. The implications clearly underscore why early and sustained gum disease treatment is so vital.
Systemic Health Risks Linked to Untreated Gum Disease
Left untreated, gum disease is much more than a localized problem. Mounting scientific evidence links this oral infection to a spectrum of systemic issues, from cardiovascular disease to diabetes, pregnancy complications, and respiratory conditions. As the soft tissue and bone recede, harmful bacteria and their inflammatory byproducts may travel through the bloodstream, triggering widespread inflammation—often silently and without early symptoms.
For at-risk populations, the dangers are even more pronounced. People with underlying health conditions should prioritize gum disease treatment to mitigate both dental and broader medical risks. Addressing oral infections promptly may play a powerful role in maintaining your overall well-being and improving quality of life.

“Early intervention with the right treatment options for gum disease can prevent tooth loss and support your overall well-being.” — Dr. Brian Walsh
Emerging and Future Trends in Gum Disease Treatment
The landscape of gum disease treatment continues to evolve, bringing sharper technology and more personalized medicine into daily care. Modern dental practitioners now employ minimally invasive tools that target infections precisely, reduce healing times, and deliver better patient experiences. In tandem, research into genetic and microbiome differences is paving the way for treatments that truly fit the unique makeup of each individual.
Understanding these trends means patients can look forward to procedures that preserve more natural tissue, reduce discomfort, and achieve more reliable results. Staying informed about the direction of periodontal therapies empowers you to choose the safest, most effective solutions available today and in the future.
Laser Therapy and Minimally Invasive Disease Treatment
Laser therapy represents one of the most exciting advances in periodontal care. By using targeted light energy, dental professionals can precisely eliminate infected tissue and bacteria within periodontal pockets—often with less discomfort and faster recovery compared to traditional methods. Minimally invasive lasers also care for surrounding healthy structures, supporting regeneration and minimizing collateral tissue damage.
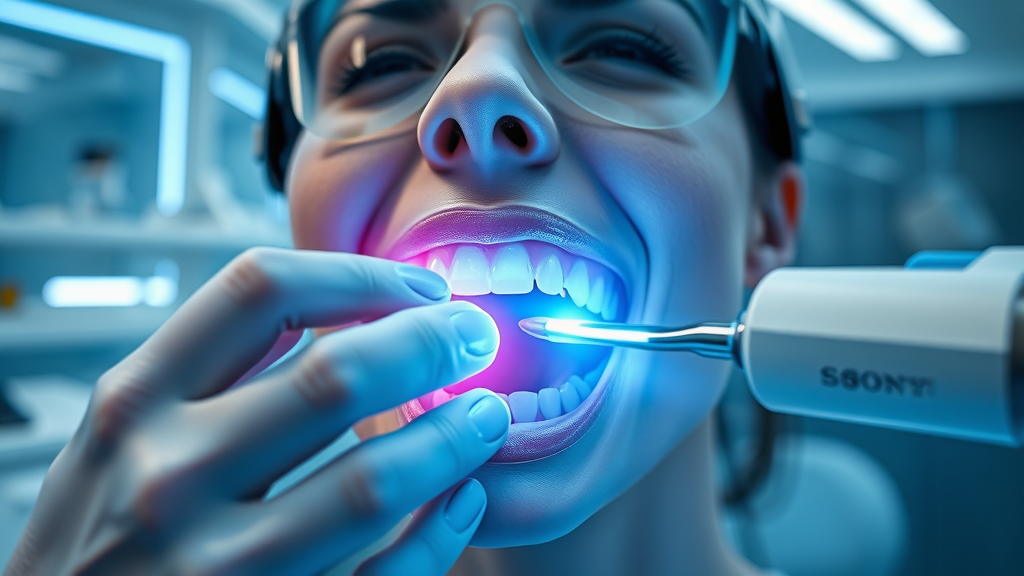
Patients undergoing minimally invasive gums disease treatments typically experience less bleeding and swelling, require fewer stitches, and resume normal activities much sooner. Laser surgery is especially promising for those anxious about conventional surgical techniques or for those seeking the latest in high-quality gum disease management. Always discuss with your dental provider whether this approach is appropriate for your unique needs.
Personalized Medicine in Periodontal Disease Care
Personalized care is a fast-growing component of periodontal disease management. Advances in diagnostic technology now allow dentists to tailor treatment options for gum disease based on a patient’s genetic profile, immune response, or specific oral microbiome. This means that people at higher risk for rapid disease progression or suboptimal healing may benefit from custom strategies—ranging from targeted medications to advanced tissue regenerative therapies.
The future holds even more promise: as science deepens our understanding of how lifestyle, medical conditions, and genetics interact, providers can offer plans that are both more precise and more effective. By embracing these individualized approaches, patients benefit from shorter treatments, improved outcomes, and a greater likelihood of sustained oral health.
Early detection offers more treatment options for gum disease
Both surgical and non-surgical solutions exist
Prevention and maintenance are critical
Interview: Gum Disease Treatment Success Stories and Patient Experiences
What is the best treatment for gum disease?
The best treatment options for gum disease depend on its stage and severity. For mild cases, improved oral hygiene and professional cleanings may be enough. For moderate to advanced stages, deep cleaning methods like scaling and root planing , medications, and surgical options such as pocket reduction surgery , gum graft procedures, or bone grafting may be necessary. A dentist can personalize treatment according to individual needs for optimal outcomes.
How long can you keep your teeth with periodontal disease?
With consistent gum disease treatment —including early intervention, proper maintenance, and professional monitoring—many people can retain their teeth for life, even with a history of periodontal disease. The length of tooth retention depends on disease severity, patient compliance, presence of risk factors , and the success of both at-home and clinical therapies. Delaying care, however, increases the likelihood of tooth loss.
Can a gum score of 4 be reversed?
A gum score of 4 indicates moderate periodontal pockets and gum inflammation. While some improvement in gum health and reduction in inflammation is possible with professional scaling and root planing and excellent daily oral hygiene, established bone and tissue loss may not be entirely reversible at this stage. However, stabilizing the condition and preventing further progression is achievable with timely and diligent care.
How to cure a gum infection without a dentist?
While you can support oral health by brushing, flossing, and using antimicrobial mouth rinses, truly curing a gum infection without professional help is not advised. Only a dentist can fully remove plaque and tartar beneath the gums and safely treat advanced infections. Attempting to manage severe symptoms at home can result in disease progression and increased complication risk.
Frequently Asked Questions About Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Can treatment options for gum disease really reverse damage? Early-stage damage from gingivitis can often be reversed with proper care. More severe loss of bone or gum tissue might be stabilized or partially restored using advanced therapies, but complete reversal isn't always possible.
How long does gum disease treatment take? Treatment length varies from a few weeks for mild cases to several months for advanced disease, especially if surgery or regenerative procedures are required. Maintenance is lifelong for optimal results.
Which gum disease treatments are covered by insurance? Basic professional cleanings and some non-surgical therapies are usually covered. Coverage for surgical procedures like gum graft or bone grafting may vary, so check with your insurance provider.
Is laser periodontal disease treatment safe and effective? Laser therapy is considered safe and is effective for many patients, offering precise infection removal and faster healing in select situations. Suitability may depend on individual diagnosis and practitioner experience.
Comprehensive Approach: Combining Treatment Options for Gum Disease for Optimal Results
An optimal gum disease management strategy blends professional interventions with ongoing at-home prevention. Regular dental evaluations, advanced surgical or non-surgical treatments as indicated, and diligent homecare together provide the best defense against progression and recurrence. Coordinating these options with your provider ensures the highest standard of lifelong oral health.
Patient Testimonial: Transforming Smiles with the Right Treatment Options for Gum Disease
Connect with Experts for Gum Disease Treatment in Johnstown and Neighboring Communities
Ready to take control of your oral health ? Contact the specialized team at Johnstown Dental Care for a consultation on the best treatment options for gum disease in Johnstown, New Albany, Granville, Alexandria, Pataskala, and surrounding areas in Licking County, Franklin County, and Delaware County.
Johnstown Dental Care
370 West Coshocton St.
Johnstown, OH 43031
Phone: (470) 967-6046
Website: www.johnstowndentalcare.com
Conclusion
Act swiftly: adopt preventive care at home, seek early professional treatment, and consult dental experts to preserve your smile and overall health. Start your journey toward healthier gums today!
If you’re interested in taking a broader approach to your oral health beyond gum disease treatment, consider how modern orthodontic solutions can further enhance your smile and confidence. Today’s clear aligner options offer a discreet and effective way to address misalignment, which can also contribute to healthier gums and easier cleaning. To discover how aligning your teeth can complement your periodontal care and elevate your overall dental wellness, explore the latest advancements in modern orthodontics . Embracing a comprehensive strategy ensures your smile remains both healthy and beautifully aligned for years to come.
To further enhance your understanding of gum disease treatments, consider exploring the following authoritative resources:
The Cleveland Clinic’s article, “ Gum Disease Treatment ,” provides a comprehensive overview of both non-surgical and surgical options, detailing procedures like scaling and root planing, antibiotic therapies, and various surgical interventions.
Healthline’s piece, “ Periodontal Treatment: Surgical and Other Options ,” offers insights into the progression of periodontal disease and the corresponding treatments, including deep cleaning methods and advanced surgical techniques.
These resources offer in-depth information to help you make informed decisions about managing and treating gum disease effectively.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment