Did you know that up to 30% of adolescents show early signs of dental erosion, making it one of the most widespread yet preventable oral health issues globally? If you or your loved ones enjoy fruit juices, carbonated drinks, or suffer from frequent acid reflux, your teeth could be at risk right now for irreversible enamel damage. Tooth erosion doesn’t always hurt in the early stages, but the consequences can be lifelong. Get ahead of the problem—keep reading to fully understand what is tooth erosion, how to spot it, and what you can do to safeguard your smile.
Unveiling the Facts: Startling Statistics on Tooth Erosion and Dental Erosion
"Up to 30% of adolescents exhibit early signs of dental erosion, making it one of the most prevalent oral health issues today."
What You'll Learn About What is Tooth Erosion
- The definition and causes of tooth erosion
- How dental erosion impacts tooth enamel and tooth surface
- Differences between tooth erosion, enamel erosion, and tooth decay
- Prevention, symptoms, and treatment options for tooth erosion
- Frequently asked questions on tooth surface loss
Understanding What is Tooth Erosion: Definitions and Core Concepts
Dental Erosion vs. Tooth Erosion vs. Enamel Erosion
The terms tooth erosion, dental erosion, and enamel erosion are closely related, but they spotlight different aspects of tooth wear. Dental erosion describes the process by which acids, typically not originating from bacteria, gradually dissolve the hard surfaces of the teeth. Tooth erosion broadly covers the irreversible loss of tooth substance caused by acid attack, affecting both the dentin and the outer enamel surface. Enamel erosion, meanwhile, hones in specifically on the loss of the outermost, shield-like layer of your teeth—your enamel—which serves as the main defense against tooth decay and sensitivity. It's important to know that while tooth decay is triggered mainly by bacteria, erosion is all about acid from foods, drinks, or your own body. This subtle but important distinction affects the way dentists diagnose and treat these issues, and it guides your preventive care at home.
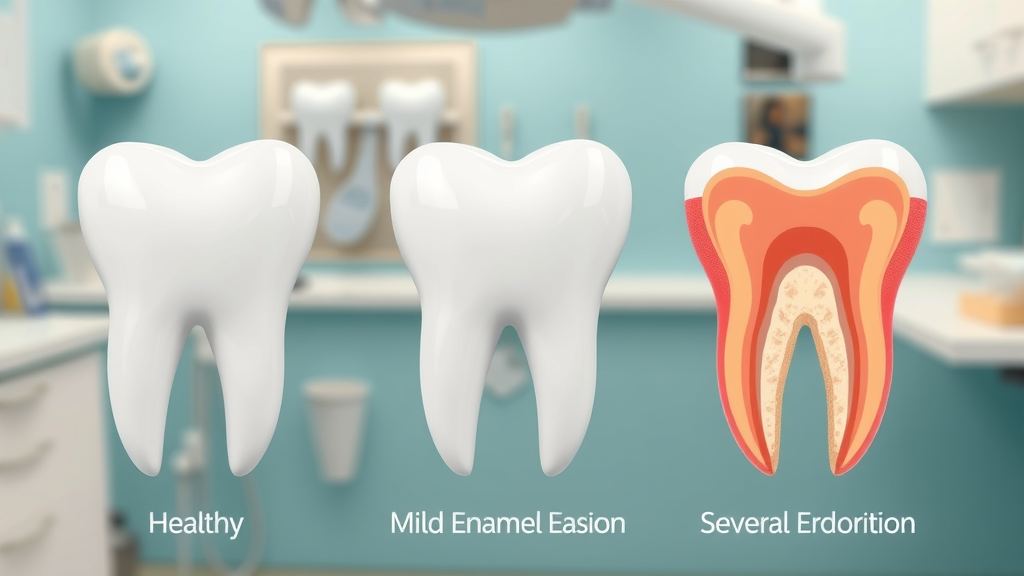
How Tooth Surface and Tooth Enamel Are Affected
The tooth enamel is the hardest tissue in your body, but it's not invincible. When acid repeatedly contacts the teeth, it dissolves essential minerals from the surface, causing the enamel to soften and gradually wear away. Over time, this process leads to tooth surface loss—the enamel gets thinner, the underlying dentin becomes exposed, and the teeth may look yellower or more translucent. As this cycle continues, your teeth become more vulnerable to tooth decay, sensitivity, and even chipping. Once the enamel is gone, the body cannot regenerate it, which is why prevention matters so much. Understanding what tooth erosion is means recognizing these subtle changes in the tooth surface before they spiral into major dental health problems.
For individuals who have already experienced significant enamel loss or tooth surface damage, restorative solutions such as dental implants can play a crucial role in restoring both function and aesthetics. If you're interested in learning more about advanced options for replacing lost teeth, explore our comprehensive guide to dental implants in Columbus, OH and discover how modern dentistry can help rebuild your smile.
Key Causes of Tooth Erosion: Diet, Stomach Acid, and Beyond
Stomach Acid and Its Impact on Tooth Surface Loss
One of the most overlooked yet significant culprits behind tooth surface loss is stomach acid. When acidic contents from your stomach repeatedly reach your mouth—whether due to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), frequent vomiting from eating disorders, or chronic medical conditions—your enamel is exposed to hydrochloric acid, a substance far more erosive than anything found in your diet. People with reflux disease or other conditions that increase contact with stomach acid often develop pronounced dental erosion on the inside (lingual surfaces) of their teeth. This kind of erosion is especially concerning because it's usually more severe, and regular brushing cannot reverse the loss of tooth enamel. Early detection and medical intervention are key to protecting both your oral and overall health.
Dietary Factors Contributing to Dental Erosion
What you eat and drink plays a leading role in the development of enamel erosion. Frequent exposure to acidic drinks like soda, sports beverages, energy drinks, and fruit juices can soften enamel, making it more susceptible to tooth wear. Regular consumption of acidic foods—think citrus fruits, sour candies, and pickled products—also contributes to gradual enamel breakdown. The harm is compounded when harmful dietary habits are paired with dry mouth (often from medications or dehydration), which limits saliva’s natural ability to neutralize acids and remineralize teeth. This makes it crucial to be aware of your patterns: sipping on juice continuously throughout the day, drinking soda with every meal, or snacking on vinegar-based treats may seem harmless, but these habits are key drivers of dental erosion.
- Acidic drinks (soda, fruit juices)
- Frequent consumption of sour foods
- Medical conditions causing acid reflux

Everyday Habits That Accelerate Enamel Erosion
It’s not just dietary choices or medical conditions—everyday routines can quietly speed up enamel erosion. Brushing too hard, particularly right after consuming acidic foods and drinks, can scrub away softened enamel and exacerbate tooth surface loss. Chewing on hard objects like ice, pens, or finger nails causes microscale cracks that weaken the tooth enamel. Habits such as sipping on acidic beverages for extended periods, swishing drinks in the mouth, and not rinsing with water after meals all create environments where enamel is under continuous acid attack. Over time, these behaviors contribute as much to tooth erosion as any dietary pattern, highlighting the importance of mindful oral care and routine dental visits.
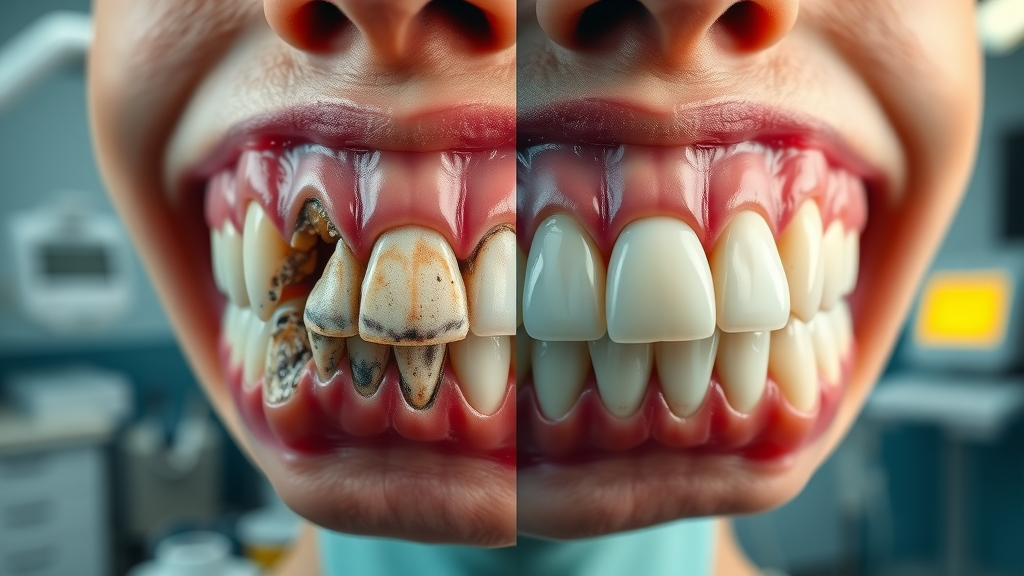
What Does Tooth Erosion Look Like? Signs and Symptoms of Dental Erosion
- Visible changes in tooth color
- Rounded teeth edges
- Tooth surface loss and increased transparency
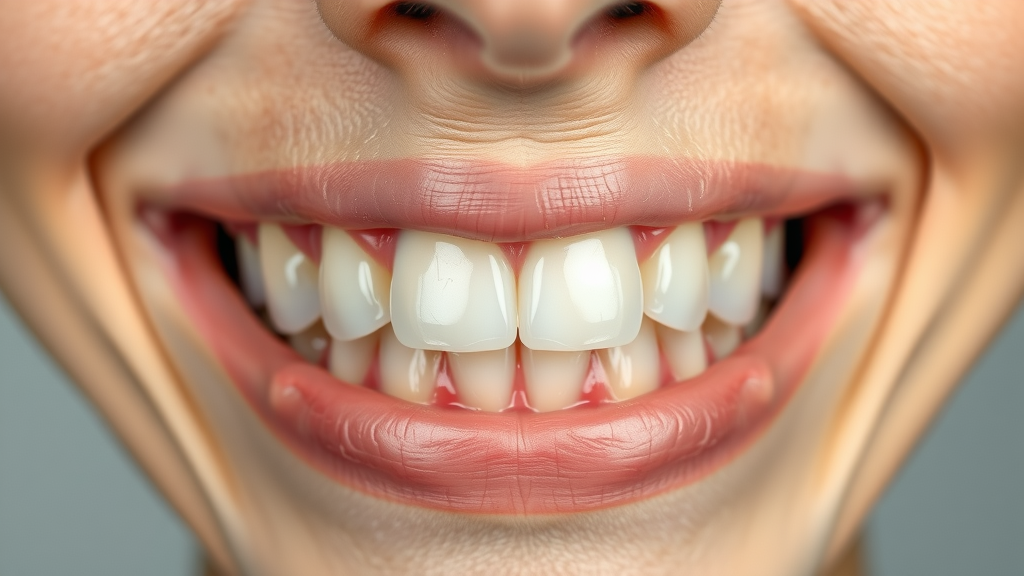

How to Identify the Early Stages of Enamel Erosion
Early enamel erosion may go unnoticed since it doesn’t immediately cause pain. One of the first signs can be a change in tooth color, from white to a duller yellow as the enamel thins and the underlying dentin shows through. Patients might also notice smooth, shiny surfaces on the teeth, especially on the occlusal surfaces and edges. Transparent or glassy edges, rounded contours, notches near the gumline, or heightened sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods are clear indicators that the erosion process is underway. As damage progresses, more obvious symptoms such as tooth chipping, pain, and increased tooth wear will become apparent. Identifying tooth erosion at an early stage offers the best chances for successful prevention and management.
| Stage | Symptoms | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Initial | Mild discoloration, surface dullness | Minimal discomfort |
| Moderate | Transparent edges, sensitivity to sweets/temperature | Noticeable wear |
| Severe | Surface loss, pain, chipping | Compromised tooth structure |
What is the Connection Between Tooth Erosion and Tooth Decay?
Surface Loss: Erosion vs. Tooth Decay
Tooth erosion and tooth decay may both lead to surface loss, but their causes and effects differ. Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, primarily results from acids produced by bacteria feeding on sugars in the mouth, gradually destroying the hard and soft tissues of the tooth. In contrast, dental erosion is non-bacterial and is due to direct acid attack from dietary or internal sources like stomach acid or acidic beverages. Both conditions result in the breakdown of hard tissues, leading to sensitivity, cavities, and, eventually, the potential loss of tooth structure. It's important to understand these differences to receive proper treatment—the approaches for managing erosion and decay are not identical and often need to be combined for optimal oral health.
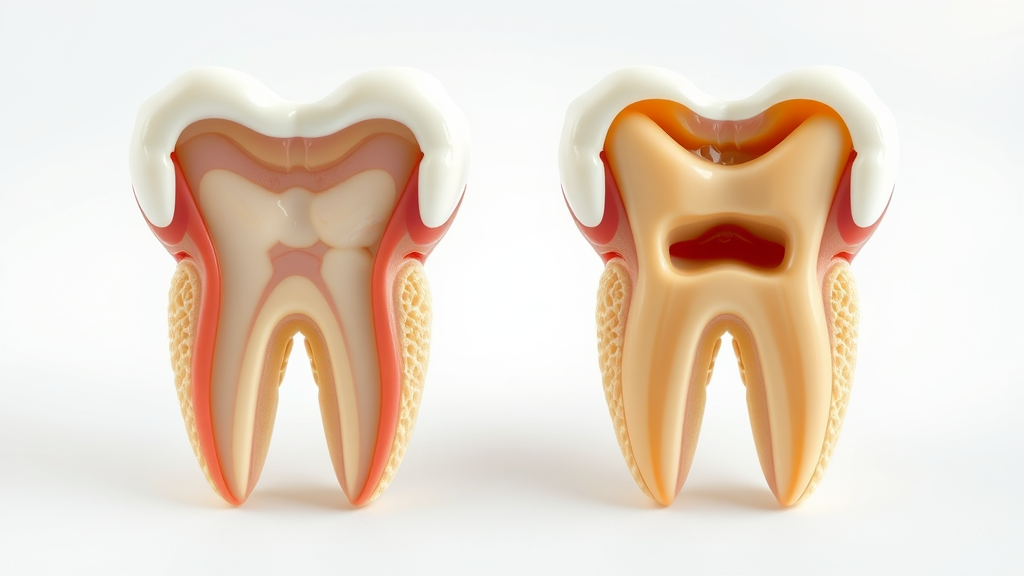
How Enamel Erosion Increases the Risk of Loss of Tooth
As enamel erosion progresses, the protective barrier of your teeth becomes thin or lost completely, exposing the softer, more sensitive dentin beneath. This makes the teeth more vulnerable to attacks by bacteria, accelerating the risk of tooth decay and, in severe cases, even loss of tooth. Without timely intervention, what may start as slight sensitivity can end with structural breakdown, infection, and ultimately, tooth extraction. Thus, recognizing signs of tooth surface loss and seeking dental care promptly not only preserves aesthetics and comfort but may also prevent more serious and costly consequences.
How Do Dentists Diagnose Tooth Erosion and Dental Erosion?
Clinical Exams: Assessing Tooth Surface and Dental Erosion
Accurate diagnosis of tooth erosion requires a detailed clinical exam. Dentists inspect the teeth for characteristic signs such as dullness, enamel thinning, changes in texture, and peculiar wear patterns unrelated to decay or physical abrasion. Attention is paid to areas typically affected by acid: the palatal (inside) surfaces for patients with acid reflux, the occlusal (chewing) surfaces in heavy soda drinkers, and smooth surfaces near the gumline. These evaluations sometimes include special dyes or lights to outline surface loss not easily seen by the naked eye. Documenting the appearance and progression of erosion helps to distinguish it from other forms of tooth wear—like abrasion or attrition—and guide effective prevention or restoration strategies.
Digital Imaging and Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For a comprehensive assessment, dentists often use digital imaging tools such as intraoral cameras, digital X-rays, and 3D scanners. These technologies provide high-resolution images that reveal the precise extent of enamel erosion and surface loss. Advanced tools can even track erosion progression over time, monitor responses to treatment, and offer detailed visualization for patient education. In complex cases, further analysis can include quantitative light-induced fluorescence and scanning electron microscopy, helping differentiate between physical and chemical forms of tooth wear. The integration of technology not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also empowers you to take control of your oral health with visual feedback and tailored solutions.
Treatment Options: Can Tooth Erosion Be Fixed?
Remineralization and Enamel Repair
Once lost, your body cannot regrow enamel. However, early tooth erosion can be slowed or stabilized by remineralization strategies. Dentists may recommend special fluoride treatments, prescription pastes, or products containing calcium and phosphate ions, all designed to replenish minerals in mildly affected enamel. These treatments help harden the surface, reduce sensitivity, and minimize further enamel erosion. While remineralizing products are highly effective in the early stages, beyond minor surface loss, restorative procedures are necessary to rebuild strength, function, and beauty.
Dental Restorative Procedures for Enamel and Surface Loss
If tooth erosion has led to significant surface loss or compromised aesthetics, restorative dental solutions may be recommended. These range from conservative treatments like dental bonding—where tooth-colored resin is applied to repair minor defects—to more advanced interventions such as veneers or crowns which cover and protect entire tooth surfaces. In-office fluoride applications are often part of the regimen to protect adjacent teeth from progressing enamel erosion. The approach depends on the location, severity, and appearance of the erosion. The goal is always the same: restore your smile’s health, prevent further tooth wear, and maintain natural function as long as possible.
- Fluoride treatments
- Dental bonding
- Veneers
- Crowns
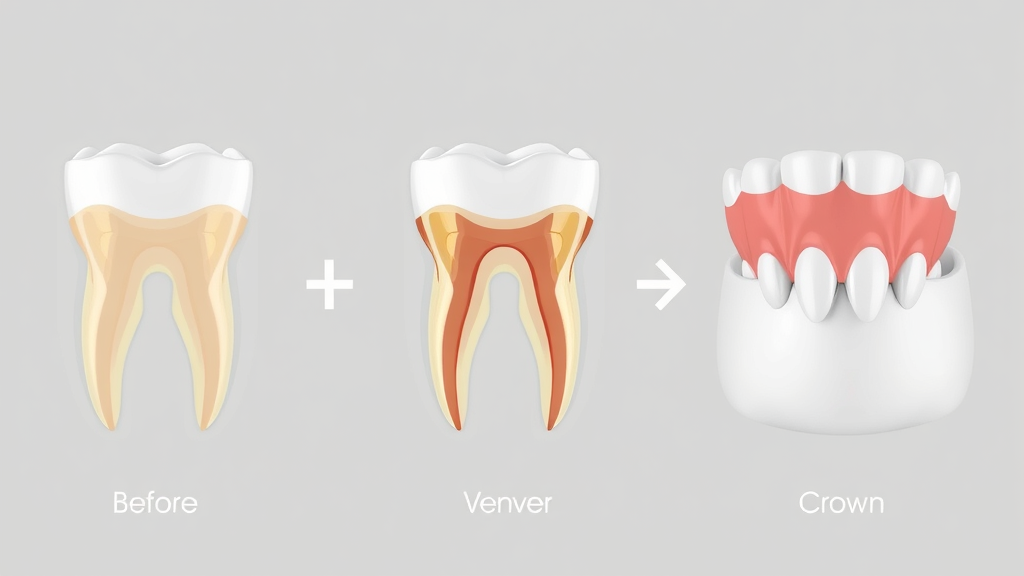
Ongoing Prevention of Tooth Erosion and Dental Erosion
Effective management of tooth erosion doesn’t end with repair. Ongoing prevention is crucial to keep dental erosion at bay. This means regular dental checkups for monitoring, consistent use of fluoride or remineralizing products as prescribed, and lifestyle changes to minimize acid exposure. Dentists often create individualized maintenance plans that might include dietary guidance, special toothpastes, and custom-formed mouthguards for patients with reflux or bruxism. Vigilance at home, coupled with professional support, makes a substantial difference in protecting your tooth enamel for life.
Best Practices for Preventing Enamel and Tooth Erosion
- Limit acidic food and drinks
- Rinse with water after consuming acids
- Maintain proper oral hygiene
- Schedule regular dental checkups
"Addressing tooth erosion early is key to maintaining lifelong oral health." – Dr. Susan Lee, DDS
Key Takeaways: Protecting Tooth Enamel and Preventing Tooth Erosion
- Tooth erosion is irreversible, so prevention is crucial.
- Dental erosion can progress rapidly without intervention.
- Proper dental care can manage and limit further enamel erosion.

People Also Ask: Your Top Questions on What is Tooth Erosion
What is erosion of the teeth?
Answer: Erosion of the teeth, also known as dental erosion, is the progressive loss of tooth enamel caused by acid attack. This leads to thinning and eventual loss of the tooth surface.
What does erosion look like in teeth?
Answer: Erosion typically presents as thinning, yellowing, or transparency at the edges of teeth, with a smooth, shiny appearance and sometimes rounded or notched edges.
Can tooth erosion be fixed?
Answer: While early tooth erosion can't be reversed, it can be managed. Severe enamel loss may need restorative treatments such as bonding, crowns, or veneers.
What does tooth erosion feel like?
Answer: Tooth erosion can make teeth feel sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks. In advanced cases, discomfort and pain are common.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About What is Tooth Erosion
- Does tooth erosion always cause pain?
- Can children experience dental erosion?
- What are the long-term effects of tooth erosion?
- How often should I see a dentist to monitor tooth enamel?
Watch this animated educational video for a visual explanation of tooth erosion, how acid attacks the enamel, the difference between healthy and eroded teeth, and key prevention tips.
This video explores the connection between dietary habits, acid reflux, and their combined impact on tooth surface and enamel integrity.
Conclusion: Take Action Against Tooth Erosion Today
"Protect your smile by understanding what is tooth erosion and taking proactive steps to safeguard your enamel."
Understanding tooth erosion is just one part of maintaining lifelong oral health. If you’re interested in a more comprehensive approach to restoring your smile and ensuring lasting dental wellness, consider exploring the broader benefits of advanced restorative solutions. Our resource on dental implants in Berkshire, OH delves into how modern implant dentistry can transform not only your appearance but also your confidence and quality of life. Take the next step in your oral health journey and discover how innovative treatments can help you achieve a resilient, beautiful smile for years to come.
Contact Johnstown Dental Care: Your Partners in Preventing Tooth Erosion
- Address: 370 West Coshocton St. Johnstown, OH 43031
- Phone: (470) 967-6046
- Website: www.johnstowndentalcare.com
- Proudly serving: Johnstown, New Albany, Granville, Alexandria, Pataskala, and surrounding areas in Licking, Franklin, and Delaware Counties.
To enhance your understanding of tooth erosion, consider exploring the following authoritative resources:
-
The American Dental Association’s article, “Dental Erosion,” provides a comprehensive overview of the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures associated with dental erosion.
-
Healthdirect’s guide, “Dental erosion - symptoms, treatments and causes,” offers detailed insights into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for dental erosion, emphasizing the importance of early detection and management.
If you’re serious about protecting your dental health, these resources will equip you with the knowledge to prevent and address tooth erosion effectively.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment